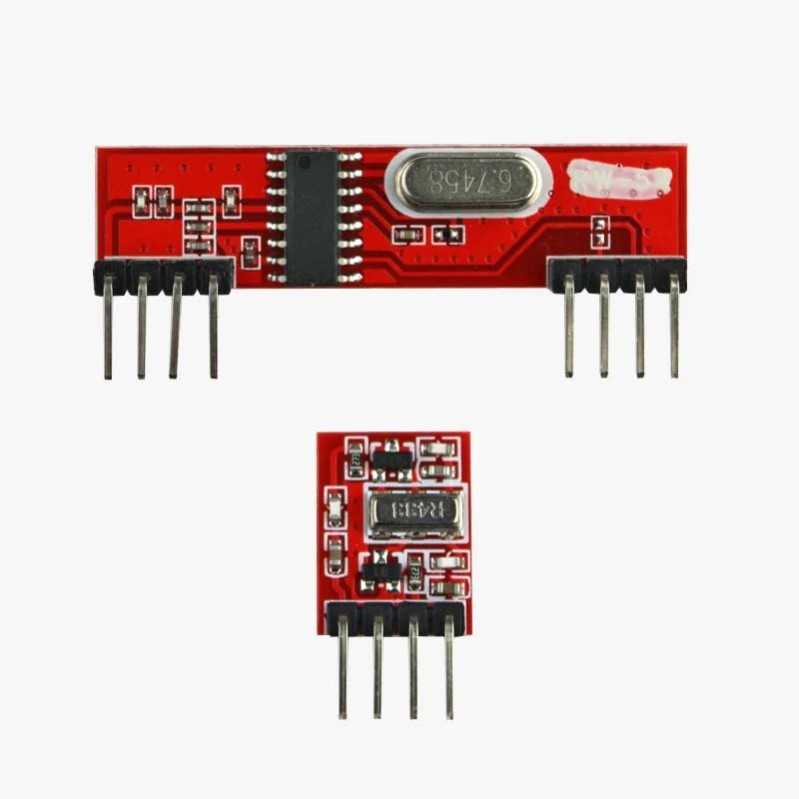








RF 4.33 Mzh TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER PAIR
This RF module is a combination of RF Transmitter and RF Receiver. The transmitter/receiver (Tx/Rx) pair operates at a frequency of 433 MHz. The RF transmitter receives serial data and transmits it wirelessly through through its RF antenna. The transmission occurs at the rate of 1 Kbps – 10 Kbps.
₹ 104 ₹149
149


| Made In : | India |
Add FAQ
An RF 433 MHz transmitter and receiver pair is commonly used in wireless communication projects for various applications, including remote controls, wireless data transmission, and simple telemetry. The 433 MHz frequency is popular due to its balance between range and power consumption.
Key Features:
-
Frequency:
- 433 MHz: This is the frequency at which the transmitter and receiver communicate. It's a popular choice for many low-power, short-range communication systems.
-
Transmitter:
- Function: Converts data into a radio frequency signal and transmits it wirelessly.
- Modulation: Typically uses amplitude modulation (AM) or on-off keying (OOK).
-
Receiver:
- Function: Receives the RF signal and converts it back into data.
- Sensitivity: The ability of the receiver to detect weak signals and convert them into readable data.
-
Power Supply:
- Voltage: Often operates at 3.3V or 5V. Check the specifications to match your power supply.
-
Communication Range:
- Distance: Typically ranges from 50 meters to a few hundred meters depending on the environment, antenna quality, and power output.
Applications:
-
Wireless Remote Controls:
- Devices: Used in remote controls for appliances, garage doors, and other home automation devices.
-
Wireless Sensors:
- Data Transmission: Useful for transmitting data from wireless sensors to a central receiver.
-
Remote Data Logging:
- Telemetry: For projects requiring remote data collection and transmission.
-
Simple Wireless Communication:
- Prototyping: Ideal for hobbyists and engineers creating simple wireless communication systems.
Selecting the Right Pair:
-
Frequency Band:
- 433 MHz: Ensure that both the transmitter and receiver operate on the same frequency.
-
Modulation Scheme:
- Match Modulation: Verify that the transmitter and receiver use compatible modulation schemes (OOK or AM).
-
Range Requirements:
- Distance: Choose based on the required communication range. Keep in mind that range can be affected by obstacles and interference.
-
Power Supply:
- Voltage: Ensure the operating voltage of the transmitter and receiver matches your power supply.
-
Antenna:
- Quality: The quality of the antenna affects range and signal strength. Use a properly tuned antenna for best performance.
Installation and Usage:
-
Wiring:
- Connections: Connect the transmitter and receiver to your microcontroller or other electronic devices. Common connections include:
- Transmitter: VCC, GND, DATA (to transmit data).
- Receiver: VCC, GND, DATA OUT (to receive data).
- Connections: Connect the transmitter and receiver to your microcontroller or other electronic devices. Common connections include:
-
Antenna Setup:
- Attach Antennas: Connect suitable antennas to the transmitter and receiver to enhance range and performance.
-
Testing:
- Verify Communication: Test the communication by sending data from the transmitter and checking for proper reception at the receiver.
-
Programming:
- Microcontroller: Write and upload code to your microcontroller to handle data transmission and reception.
Maintenance Tips:
-
Check Connections:
- Secure Wiring: Ensure all connections are tight and properly connected.
-
Inspect for Interference:
- Avoid Obstructions: Keep the transmitter and receiver away from large metal objects and other sources of interference.
-
Monitor Power Supply:
- Stable Voltage: Ensure a stable power supply to prevent communication issues.
Purchasing:
- Retailers: Available from electronics suppliers, online retailers like Amazon, eBay, and specialized RF component suppliers.
- Specifications: Verify the frequency, voltage, modulation type, and range to match your project requirements.
Example Products:
-
RF 433 MHz Transmitter and Receiver Module:
- Frequency: 433 MHz.
- Modulation: OOK or AM.
- Voltage: Typically 3.3V or 5V.
-
433 MHz Wireless Transmitter and Receiver Pair Kit:
- Includes: Both transmitter and receiver modules.
- Accessories: Often includes antennas and may come with documentation.
-
RF Link Kit 433 MHz:
- Features: Includes transmitter, receiver, and sometimes additional components for easy integration into projects.
By selecting the appropriate 433 MHz RF transmitter and receiver pair and setting them up correctly, you can achieve reliable wireless communication for your projects, enhancing flexibility and functionality in your designs.

0 Reviews For this Product












.jpg&width=225&quality=80)
