

.jpg&width=620&quality=80)


.jpg&width=172&quality=80)


.jpg&width=300&quality=80)
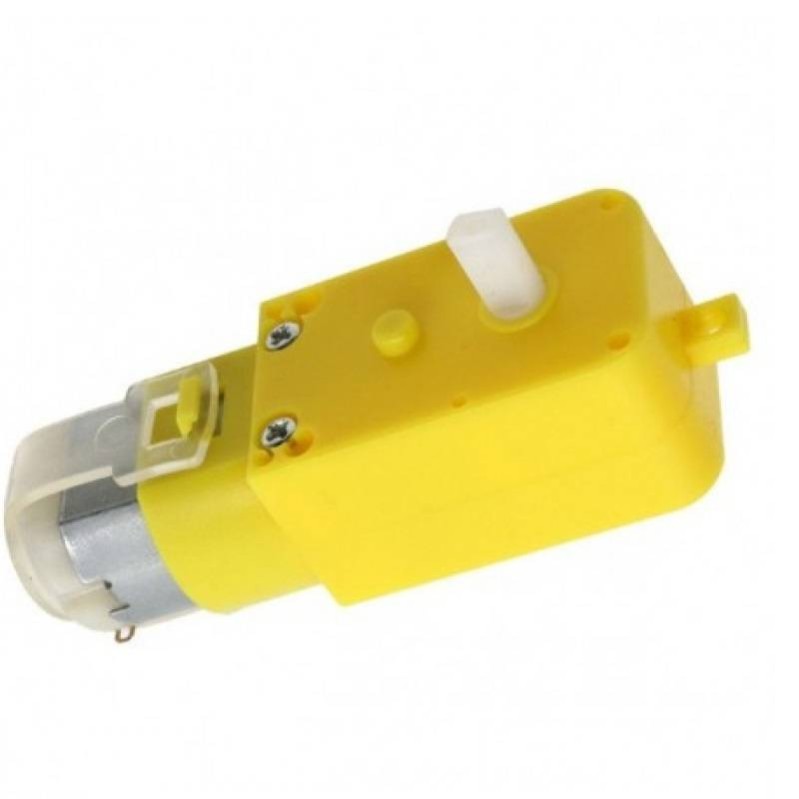
100 RPM BO Motor single shaft
The 100 RPM Dual Shaft BO Motor is a straight motor which gives good torque and RPM at lower operating voltages. It is a low-cost geared DC Motor. It is an alternative to metal gear DC motors. The 65MM Wheel is made up of high-quality rubber.
₹ 42 ₹99
99


| Voltage : | 12v dc |
| Made In : | India |
Add FAQ
A 100 RPM straight DC geared motor is a specific type of DC motor that is equipped with a gearbox to reduce its speed to 100 revolutions per minute (RPM). This type of motor is commonly used in applications where precise, slow-speed control and higher torque are required.
Key Features and Specifications:
-
Voltage:
- Typically 12V DC: This is the most common voltage for such motors, though they can also be available in other voltages like 6V or 24V depending on the application requirements.
-
Speed:
- 100 RPM: The output speed of the motor after the gear reduction. This is significantly slower than the motor's no-load speed, thanks to the gearbox.
-
Gearbox:
- Gear Reduction: The motor includes a gearbox that reduces the speed of the motor's shaft while increasing the torque. The gear ratio of the gearbox determines the reduction from the motor's no-load speed to the final output speed of 100 RPM.
- Type of Gears: Common types include spur gears, planetary gears, or worm gears, each offering different benefits in terms of torque, efficiency, and compactness.
-
Torque:
- High Torque: Due to the gear reduction, the motor can provide high torque at low speeds. This is essential for applications that require significant mechanical force, such as robotics and conveyor systems.
-
Motor Type:
- Brushed DC Motor: Most commonly used in such setups. It has brushes and a commutator that handle the switching of current in the motor windings.
- Brushless DC Motor: Less common for geared motors but provides higher efficiency and longer life with electronic commutation.
-
Construction:
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor that creates the magnetic field.
- Rotor: The rotating part that turns due to the interaction with the magnetic field.
- Commutator and Brushes (for Brushed Motors): Used to switch the current direction in the rotor windings.
-
Applications:
- Robotics: For precise movements and control of mechanical parts.
- Automated Systems: Such as conveyor belts and actuators where controlled, slow motion is required.
- Model Vehicles: For slow-moving parts or steering mechanisms.
- Consumer Appliances: In devices requiring controlled and consistent movement.
Technical Specifications:
Typical specifications for a 100 RPM straight DC geared motor might include:
- Voltage: 12V DC (can vary)
- Output Speed: 100 RPM (at rated voltage)
- No-Load Speed: Higher RPM before gear reduction (depends on motor design)
- Stall Torque: Varies depending on the motor and gearbox; often specified in units like Nm (Newton-meters) or oz-in (ounce-inches)
- Current Consumption: Varies with load; typically higher under stall or heavy load conditions
- Gear Ratio: The ratio of the motor's no-load speed to the output speed of 100 RPM determines the gear ratio. For instance, if the motor's no-load speed is 2000 RPM, the gear ratio would be 20:1.
Wiring and Operation:
Wiring Diagram:
-
Power Supply:
- Positive Terminal (+): Connects to the positive terminal of the DC power supply.
- Negative Terminal (–): Connects to the negative terminal of the DC power supply.
-
Motor Control:
- Direct Control: For basic on/off operation, connect the motor directly to the power supply.
- Speed Control: Can be achieved using a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal if speed adjustment is needed.
0 Reviews For this Product





3.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)







