1.jpeg)
1.jpg&width=620&quality=80)
1.jpeg&width=175&quality=80)
1.jpg&width=172&quality=80)
1.jpeg&width=300&quality=80)
1.jpg&width=300&quality=80)
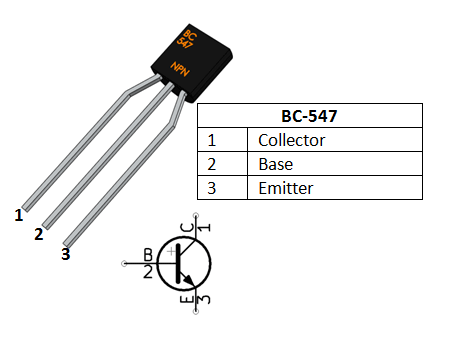
BC547 Transistor
The BC547 is a widely used NPN (negative-positive-negative) bipolar junction transistor (BJT), primarily used for general-purpose amplification and switching applications in electronics. It is a small signal transistor, meaning it's typically used in low-power circuits, such as signal processing or low-current switching.
₹ 6 ₹10
10
Add FAQ
The BC547 is a widely used NPN (negative-positive-negative) bipolar junction transistor (BJT), primarily used for general-purpose amplification and switching applications in electronics. It is a small signal transistor, meaning it's typically used in low-power circuits, such as signal processing or low-current switching.
Key Features of the BC547:
- Type: NPN transistor.
- Package: It typically comes in a TO-92 package (a small, three-pin package).
- Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): 45V (the maximum voltage that can be applied across the collector and emitter without damaging the transistor).
- Maximum Collector Current (Ic): 100mA (the maximum current that can flow through the collector without damaging the transistor).
- Power Dissipation (Ptot): 500mW (the maximum power the transistor can safely dissipate).
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 110 to 800 (a measure of how much the transistor amplifies the base current to the collector current).
Pin Configuration (TO-92 package):
- Pin 1 (Emitter): The emitter is typically connected to the ground or the negative side of the circuit.
- Pin 2 (Base): The base controls the flow of current between the collector and emitter. It is the input terminal.
- Pin 3 (Collector): The collector is connected to the load and is where the amplified current flows.
Common Uses of the BC547:
-
Amplification: The BC547 is commonly used in low-power amplification circuits (audio or signal amplifiers). It is often used to amplify weak signals in applications like radio receivers, audio devices, and signal processing circuits.
-
Switching: The BC547 is used as a switch in low-power circuits. When a small current is applied to the base, it allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively acting as a switch for controlling devices such as relays, LEDs, or small motors.
-
Biasing: In analog circuits, it is used in biasing applications, such as in voltage dividers or current regulation circuits.
-
Oscillators and Timers: Used in simple oscillator or timer circuits, such as in audio signal generators or delay circuits.
-
Digital Logic: In digital circuits, the BC547 can be used as a basic switching device for logic operations, such as creating NOT gates or simple logic gates.
How the BC547 Works:
-
Base Current: When a small current (called the base current, Ib) is applied to the base of the transistor, it allows a larger current (called the collector current, Ic) to flow from the collector to the emitter. This process is known as current amplification.
-
Amplification: The relationship between the base current and the collector current is defined by the current gain (hFE). For example, if the current gain is 200 and a small base current of 1mA is applied, the collector current will be 200mA.
Basic Circuit Examples:
- Switching Application:
- In a switching application, the transistor can be used to control the current through a load (e.g., an LED or a small motor). When a voltage is applied to the base of the transistor, it turns on and allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter.
- Amplifier Circuit:
- In an amplifier circuit, the BC547 can be used to amplify a small input signal. The transistor will increase the strength of the signal, allowing it to drive larger components or produce a stronger output signal.
Limitations:
- Low Current Handling: The BC547 can only handle 100mA of collector current, which limits its use in high-power applications.
- Power Dissipation: It can only dissipate 500mW, so it’s not suitable for applications requiring significant power handling.
Conclusion:
The BC547 is a versatile and widely used NPN transistor in electronic circuits for low-power switching and amplification applications. It is suitable for general-purpose use, particularly in signal processing, low-power audio systems, and small-scale switching applications. If you need more details about circuits or applications involving the BC547, feel free to ask!
0 Reviews For this Product











2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)

