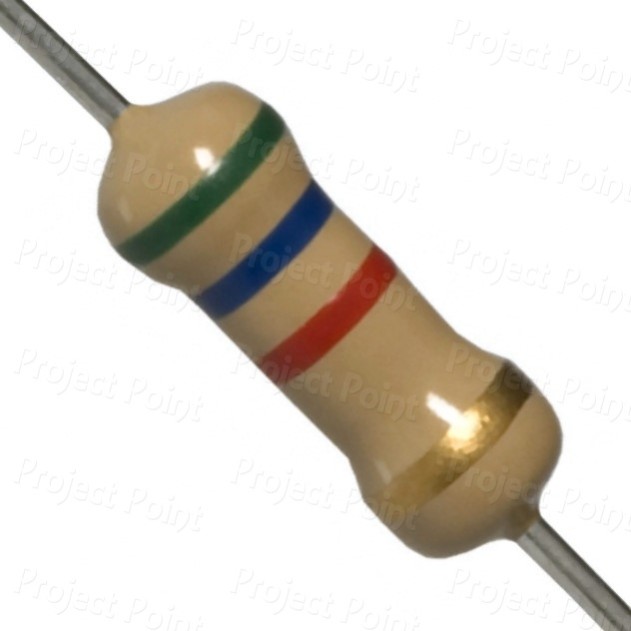






5.6k resister
5.6K Ohm 0.25W High Quality Carbon Film Resistor (CFR) with ±5% Tolerance and Tin Plated Copper Leads. 5.6K Ohm Resistor Color Code: Green, Blue, Red, Golden. Resistance: 5.6K Ohm, Power Rating: 0.25 Watt, Approximate Maximum Current: 6.68mA .
₹ 3 ₹6
6
Add FAQ
A 5.6k ohm (5.6kΩ) resistor is a commonly used resistor with a resistance value of 5,600 ohms. It is frequently found in various electronic circuits for applications that require moderate resistance, such as voltage dividers, filtering, signal conditioning, and biasing. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its specifications, uses, and considerations.
Key Specifications of a 5.6kΩ Resistor:
-
Resistance Value (5.6kΩ):
- 5.6kΩ means 5,600 ohms of resistance. This value is commonly used when you need to limit current, set voltage levels, or condition signals in a circuit.
- The resistor works according to Ohm's Law: V=I×RV = I imes R, where V is the voltage across the resistor, I is the current passing through, and R is the resistance (5.6kΩ in this case).
-
Power Rating:
- The power rating indicates how much power the resistor can safely dissipate without overheating or failing. Common power ratings for resistors include 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, and higher, depending on the application.
- A 5.6kΩ resistor will often have a 1/4W or 1/2W power rating in standard applications, but higher-power resistors are available if higher currents are expected.
-
Tolerance:
- The tolerance of a resistor indicates how much the actual resistance can deviate from its nominal value. For a 5.6kΩ resistor, typical tolerances might be ±1%, ±5%, or ±10%.
- ±1% tolerance is preferred for applications requiring greater accuracy, while ±5% and ±10% are acceptable in less precision-demanding circuits.
-
Temperature Coefficient:
- The temperature coefficient measures how much the resistance value changes with temperature. For applications that involve significant temperature fluctuations, selecting a resistor with a low temperature coefficient is important to ensure stability.
Common Applications for a 5.6kΩ Resistor:
-
Voltage Divider:
- A 5.6kΩ resistor is commonly used in voltage divider circuits to reduce a voltage from a higher level to a lower one. In combination with another resistor, it can create a desired output voltage. Voltage dividers are often used in signal conditioning, sensor interfacing, or adjusting voltage levels in a circuit.
- For example, in a 10V system, pairing a 5.6kΩ resistor with another resistor can provide a reduced output voltage to a microcontroller or sensor input.
-
Biasing Transistors:
- A 5.6kΩ resistor can be used for biasing in transistor circuits. In a common-emitter or common-collector amplifier, a 5.6kΩ resistor might be used to set the base current of a transistor, ensuring that it operates in the correct region of its characteristic curve (active or saturation region).
-
Current Limiting:
- While not as commonly used for current limiting in lower-voltage circuits as resistors with smaller values (e.g., 330Ω), a 5.6kΩ resistor can still be used for applications requiring moderate current control, such as in voltage-sensitive areas or low-power applications.
-
Pull-up or Pull-down Resistor:
- A 5.6kΩ resistor can be used as a pull-up or pull-down resistor in digital circuits. These resistors ensure that input pins of devices such as microcontrollers are in a defined state (HIGH or LOW) when not actively driven by other components.
- Pull-up resistors are often used in digital logic circuits, where a 5.6kΩ resistor might be used to pull an input to a high voltage level when no signal is present.
-
Filtering:
- A 5.6kΩ resistor can be part of an RC filter circuit. Paired with a capacitor, it can form a low-pass or high-pass filter. In these filters, the resistor helps control the cutoff frequency at which certain frequencies are attenuated or passed.
- For example, in an RC low-pass filter, the resistor (5.6kΩ) and capacitor together determine the frequency response of the filter.
-
Signal Conditioning:
- In signal conditioning circuits, a 5.6kΩ resistor can be used for impedance matching or to set gain levels. It may be part of circuits where signals need to be adapted to work with other components, such as in analog-to-digital conversion or in sensor interfacing.
-
Temperature Sensing:
- In temperature sensing circuits, a 5.6kΩ resistor could be used in combination with thermistors or thermocouples to form a voltage divider that converts temperature changes into measurable voltage changes.
-
Audio Circuits:
- In audio circuits, a 5.6kΩ resistor can be used to set levels for signal processing or to limit the current flow in signal paths to prevent distortion or damage to sensitive components.
Example Circuit:
Voltage Divider:
Suppose you want to reduce the voltage from a 12V source to 6V for a sensor that requires a 6V input. Using a 5.6kΩ resistor as one part of the voltage divider, along with another resistor, you can achieve this.
To calculate the required resistance values, use the voltage divider formula:
Vout=Vin×R2R1+R2V_{out} = V_{in} imes rac{R_2}{R_1 + R_2}
If R₁ is 5.6kΩ, and you want an output of 6V from a 12V input, you can solve for R₂:
6V=12V×R25.6kΩ+R26V = 12V imes rac{R_2}{5.6kΩ + R_2}
Solving for R₂, you get:
R2=6V12V×(5.6kΩ+R2)=0.5×(5.6kΩ+R2)R_2 = rac{6V}{12V} imes (5.6kΩ + R_2) = 0.5 imes (5.6kΩ + R_2) R2=2.8kΩR_2 = 2.8kΩ
In this case, you would pair the 5.6kΩ resistor with a 2.8kΩ resistor to get an output of 6V.
Advantages of Using a 5.6kΩ Resistor:
-
Versatility:
- A 5.6kΩ resistor is a versatile component used in a variety of circuits, including biasing, signal conditioning, voltage dividers, and filtering.
-
Availability:
- This resistor is commonly available and easy to source from electronic component suppliers.
-
Wide Range of Applications:
- The moderate resistance value of 5.6kΩ makes it suitable for use in a variety of applications, such as current limiting, voltage division, pull-up/down functions, and more.
-
Cost-Effective:
- 5.6kΩ resistors are generally inexpensive, making them a cost-effective choice for a wide range of circuits, especially in DIY and hobbyist projects.
Considerations When Using a 5.6kΩ Resistor:
-
Power Dissipation:
- When choosing a resistor, ensure the power rating is adequate for the current it will carry. In most applications, a 1/4W or 1/2W power-rated resistor will suffice, but for higher currents, a higher-rated resistor may be needed.
-
Tolerance:
- Consider the tolerance required for your application. For high-precision circuits, a ±1% tolerance resistor is preferred, while a ±5% or ±10% tolerance may suffice for more general uses.
-
Temperature Coefficient:
- In precision circuits, select a resistor with a low temperature coefficient to minimize the effect of temperature fluctuations on the resistance value.
Conclusion:
A 5.6kΩ resistor is a moderate-value resistor used in a variety of applications like voltage dividers, biasing transistors, current limiting, and signal conditioning. It offers a good balance between resistance value, power dissipation, and versatility, making it a commonly used component in electronics projects. When selecting a 5.6kΩ resistor, ensure the power rating, tolerance, and temperature coefficient are appropriate for your specific application to ensure the circuit works reliably.
0 Reviews For this Product











2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)

