
1.jpg&width=620&quality=80)

1.jpg&width=172&quality=80)

1.jpg&width=300&quality=80)
1uf 63v capacitor
Electrolytic Capacitors are polarized capacitors generally used in DC power supply circuits due to their large capacitance's and small size to help reduce the ripple voltage or for coupling and decoupling applications.
₹ 4 ₹8
8


| Made In : | India |
Add FAQ
A 1µF 63V capacitor is a capacitor with a capacitance value of 1 microfarad (µF) and a voltage rating of 63 volts (V). This type of capacitor is commonly used in a variety of electronic applications for filtering, decoupling, and timing circuits, among others. Let's explore the details, applications, and considerations associated with a 1µF 63V capacitor.
Key Specifications of a 1µF 63V Capacitor:
-
Capacitance (1µF):
- 1µF (microfarad) is a relatively small capacitance value. It means that the capacitor can store 1 microfarad (1 millionth of a farad) of charge at a given voltage. This capacitance is useful for circuits that require moderate filtering, decoupling, or signal smoothing.
-
Voltage Rating (63V):
- The voltage rating of 63V means the capacitor can safely handle up to 63 volts across its terminals. The voltage rating must always be higher than the maximum voltage the capacitor will encounter in the circuit to avoid failure.
- For example, if a capacitor is placed in a circuit with a 12V supply, a 63V capacitor would be more than adequate, providing a substantial safety margin.
-
Capacitor Type:
- 1µF 63V capacitors are commonly available in electrolytic, ceramic, and tantalum types. However, for a capacitor of this size and voltage rating, the most common types are:
- Ceramic capacitors: These are non-polarized and often used in high-frequency applications.
- Electrolytic capacitors: These are polarized and are typically used in power supply and filtering applications.
- Tantalum capacitors: These are also polarized but have a higher capacitance per unit volume, making them suitable for compact designs.
- 1µF 63V capacitors are commonly available in electrolytic, ceramic, and tantalum types. However, for a capacitor of this size and voltage rating, the most common types are:
-
Tolerance:
- The tolerance indicates how much the actual capacitance can vary from the rated value. A typical tolerance for a 1µF capacitor might be ±20%, meaning the capacitance could range from 0.8µF to 1.2µF.
-
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance):
- ESR is a measure of internal resistance in the capacitor. In some applications, especially in power supply filters, low ESR is important to avoid excessive heat generation and ensure efficient energy storage.
Common Applications of a 1µF 63V Capacitor:
-
Decoupling and Noise Filtering:
- Decoupling capacitors are placed across power lines (e.g., Vcc to ground) to filter out noise or voltage spikes. In digital circuits, a 1µF capacitor can help stabilize the voltage supply and prevent power fluctuations from affecting sensitive components like microcontrollers, logic gates, and sensors.
-
Power Supply Filtering:
- In power supplies, a 1µF 63V capacitor is often used to smooth out the voltage ripple after rectification in AC-DC power supplies. It filters high-frequency noise or ripple in the output voltage, providing a more stable DC output.
-
Timing Circuits:
- In RC circuits, a capacitor of 1µF can be combined with a resistor to create time delays, oscillators, or pulse circuits. These circuits are used in applications like timing, frequency generation, and wave-shaping.
-
Signal Coupling and Decoupling:
- A 1µF capacitor can be used in coupling applications to allow AC signals to pass through while blocking DC offsets, or in decoupling applications to isolate parts of a circuit and prevent interference.
-
Audio Applications:
- In audio circuits, a 1µF 63V capacitor may be used for filtering or coupling signals to remove unwanted frequencies and improve the quality of the sound.
-
Snubber Circuits:
- Capacitors of this size and voltage are also used in snubber circuits to suppress voltage spikes or transients that occur when switching inductive loads (like motors or relays).
-
Tuning and Frequency Response:
- In some RF circuits, capacitors like the 1µF 63V can be used in filter networks to shape the frequency response, removing or passing specific frequencies.
Example Wiring and Circuit Use Cases:
-
Power Supply Filtering:
- A typical application in power supplies is to place a 1µF 63V capacitor in parallel with the output of the rectifier circuit. This capacitor smooths the fluctuations in the DC output.
-
Decoupling in Digital Circuits:
- In microcontroller circuits, a 1µF capacitor is commonly placed across the Vcc and GND pins of the microcontroller to filter out noise from the power supply.
-
RC Timer Circuit:
- A 1µF capacitor can be used with a resistor in an RC timing circuit to create a delay or to control the frequency of oscillators.
Advantages of Using a 1µF 63V Capacitor:
-
Compact Size:
- With 1µF capacitance, the capacitor is small and can be easily used in tight spaces on a circuit board without taking up much room.
-
Wide Voltage Range:
- The 63V voltage rating gives ample overhead for most low to medium voltage circuits, making the capacitor versatile in various applications.
-
Good for Filtering:
- The 1µF capacitor is effective in filtering high-frequency noise and providing stable DC power to sensitive components, making it valuable in power supplies and sensitive analog or digital circuits.
-
Availability and Cost:
- 1µF 63V capacitors are readily available and cost-effective, which makes them a popular choice for a wide range of electronic projects.
Considerations When Using a 1µF 63V Capacitor:
-
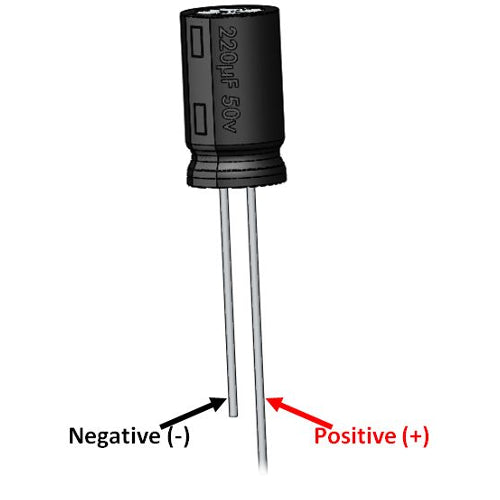
Polarity (for Electrolytic Capacitors):
- If using an electrolytic capacitor, ensure correct polarity. Electrolytic capacitors are polarized, meaning they have a positive and negative terminal. Reversing the polarity can damage the capacitor and the circuit.
-
Temperature Sensitivity:
- Capacitors degrade over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures. Ensure the capacitor operates within the recommended temperature range to maximize lifespan and performance.
-
Capacitance Tolerance:
- Tolerance of the capacitor can vary, typically by ±20%. In critical circuits, ensure that the tolerance is acceptable for the application to prevent incorrect operation.
-
ESR for Power Supply Circuits:
- In power supply applications, be mindful of the ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance). A high ESR can reduce the effectiveness of the capacitor in filtering and can cause excess heat generation.
Conclusion:
The 1µF 63V capacitor is a versatile component used in a wide variety of applications, including power supply filtering, decoupling, signal coupling, and timing circuits. It is commonly available in ceramic, electrolytic, and tantalum types, with the ceramic type being preferred for high-frequency applications. When selecting a capacitor, ensure that the voltage rating is appropriate for the circuit, and consider the tolerance, temperature rating, and ESR to ensure reliable and efficient operation in your application.

0 Reviews For this Product









2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)

