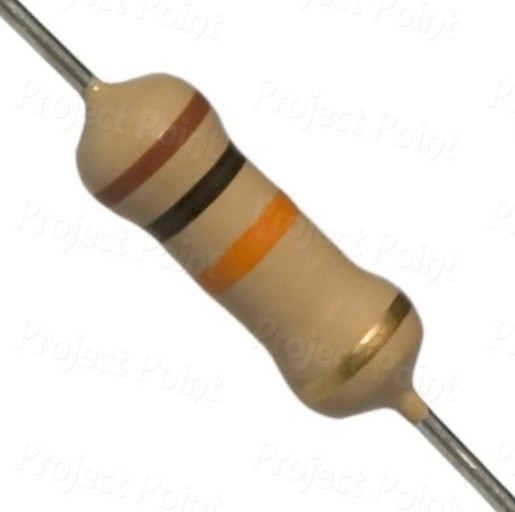





10k resister
A 10k resistor is a passive resistor with a resistance of 10,000 ohms, and is used to control the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are also known as key resistors, and are essential for the stability and safety of electronic circuits
₹ 3 ₹6
6
Add FAQ
A 10k ohm (10kΩ) resistor is one of the most commonly used resistors in electronic circuits. It provides a moderate level of resistance and has a wide range of applications in both analog and digital circuits. Here’s a detailed overview of the 10kΩ resistor, its specifications, uses, and considerations.
Key Specifications of a 10kΩ Resistor:
-
Resistance Value (10kΩ):
- The value of 10kΩ corresponds to 10,000 ohms of resistance. This resistance value is typically used in circuits to control current flow, set voltage levels, or create filters.
- The resistor follows Ohm's Law (V = I × R), meaning the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current flowing through it, with a resistance of 10kΩ.
-
Power Rating:
- The power rating of a resistor indicates how much power it can dissipate without getting damaged. Common ratings for resistors include 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, and higher.
- A 10kΩ resistor typically has a 1/4W or 1/2W power rating for general-purpose applications. For circuits with higher currents, a higher power-rated resistor may be needed.
-
Tolerance:
- The tolerance of a resistor shows how much the actual resistance value can vary from the nominal value. For example, a ±1% tolerance means the resistance could vary by 1% above or below 10kΩ.
- 10kΩ resistors often come with tolerances of ±1%, ±5%, or ±10%. Higher-precision circuits will benefit from a ±1% tolerance resistor, while less critical applications can use ±5% or ±10% tolerance resistors.
-
Temperature Coefficient:
- The temperature coefficient indicates how much the resistance changes with temperature. In applications requiring stability over temperature changes, a low temperature coefficient resistor is preferred.
- For general applications, a standard temperature coefficient is often sufficient, but for precision circuits, a resistor with a low temperature coefficient is important.
Common Applications for a 10kΩ Resistor:
-
Voltage Divider:
- A 10kΩ resistor is commonly used in voltage divider circuits, where two resistors are used to scale down a higher voltage to a lower voltage. The ratio of the resistors determines the output voltage.
- For example, if you have a 12V source and want to reduce it to 6V, you can use a 10kΩ resistor in combination with another resistor to achieve the desired output.
-
Biasing Transistors:
- A 10kΩ resistor can be used for biasing transistors in amplifier circuits. In particular, it is commonly used in the base resistor of BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) circuits to set the base current, which in turn controls the transistor’s operation.
-
Pull-up or Pull-down Resistor:
- 10kΩ resistors are frequently used as pull-up or pull-down resistors in digital circuits to ensure that input pins of microcontrollers or logic gates are in a known state (HIGH or LOW) when not actively driven by other components.
- For instance, a 10kΩ pull-up resistor can be used with a button to make the input HIGH when the button is not pressed and LOW when pressed.
-
Current Limiting:
- A 10kΩ resistor can be used in some applications to limit the current flow, though for higher current circuits, smaller resistances are typically used. For instance, it might limit the current in LED circuits or other low-power applications.
-
Filtering and Signal Conditioning:
- In RC (Resistor-Capacitor) circuits, a 10kΩ resistor can be used in combination with capacitors to create filters. This can be either low-pass, high-pass, or band-pass filters for processing analog signals.
- It can also be used in signal conditioning circuits, such as smoothing signals or providing appropriate impedance for further processing.
-
Adjusting Gain in Op-Amp Circuits:
- In operational amplifier (op-amp) circuits, a 10kΩ resistor can be part of the feedback network to set the gain of the amplifier. The feedback resistor, in combination with other resistors, helps determine the gain of the circuit.
-
Temperature Sensing:
- In some temperature-sensing circuits, a 10kΩ resistor may be used in combination with a thermistor (which has a temperature-dependent resistance). Together, they can create a voltage divider where the voltage output is proportional to the temperature.
-
Audio Circuits:
- In audio circuits, a 10kΩ resistor can be used for impedance matching and for setting the level of signals in amplifiers, tone control circuits, or in adjusting the impedance between different audio components.
Example Circuit:
Voltage Divider Example:
Suppose you want to reduce the voltage from a 12V source to 6V using a 10kΩ resistor as part of a voltage divider.
Using the voltage divider formula:
Vout=Vin×R2R1+R2V_{out} = V_{in} imes rac{R_2}{R_1 + R_2}
Where:
- Vin=12VV_{in} = 12V
- Vout=6VV_{out} = 6V
- R1=10kΩR_1 = 10kΩ
- R2R_2 is the resistor to calculate.
Solving for R2R_2:
6V=12V×R210kΩ+R26V = 12V imes rac{R_2}{10kΩ + R_2} 612=R210kΩ+R2 rac{6}{12} = rac{R_2}{10kΩ + R_2} 0.5=R210kΩ+R20.5 = rac{R_2}{10kΩ + R_2} R2=10kΩR_2 = 10kΩ
Thus, to get 6V output, you would use a 10kΩ resistor in combination with another 10kΩ resistor in the voltage divider.
Advantages of Using a 10kΩ Resistor:
-
Versatility:
- The 10kΩ resistor is versatile and used in a wide range of circuits, including voltage dividers, biasing, filtering, and signal conditioning.
-
Wide Availability:
- The 10kΩ resistor is one of the most commonly used resistors and is readily available from all major electronic component suppliers.
-
Cost-Effective:
- It is an inexpensive component that can be used in large quantities in various applications.
-
Precision:
- It’s available in various tolerances, including ±1%, which allows for precision use in more demanding applications.
Considerations When Using a 10kΩ Resistor:
-
Power Dissipation:
- Always consider the power rating for the resistor. A 1/4W resistor is common, but if your circuit draws higher current or if voltage across the resistor is high, you may need a resistor with a higher power rating (e.g., 1W).
-
Tolerance:
- For applications requiring high precision, choose a 10kΩ resistor with a low tolerance (e.g., ±1%). For general use, a ±5% tolerance resistor is typically fine.
-
Temperature Coefficient:
- In precision or high-accuracy circuits, ensure that the resistor has a low temperature coefficient to minimize resistance variation due to temperature changes.
-
Current Consideration:
- For high-current applications, a 10kΩ resistor may not be suitable as it could limit current excessively. In such cases, a smaller resistance value might be more appropriate.
Conclusion:
A 10kΩ resistor is one of the most commonly used components in electronic circuits. It has a wide range of applications, including voltage dividers, biasing transistors, current limiting, signal conditioning, and feedback networks in amplifiers. It is available in various tolerances, power ratings, and temperature coefficients to meet the needs of both general-purpose and precision applications. Always ensure the resistor's power rating, tolerance, and temperature coefficient are appropriate for your specific circuit requirements.
0 Reviews For this Product











2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
2.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)
.jpeg&width=225&quality=80)

