Product Description (Detailed):
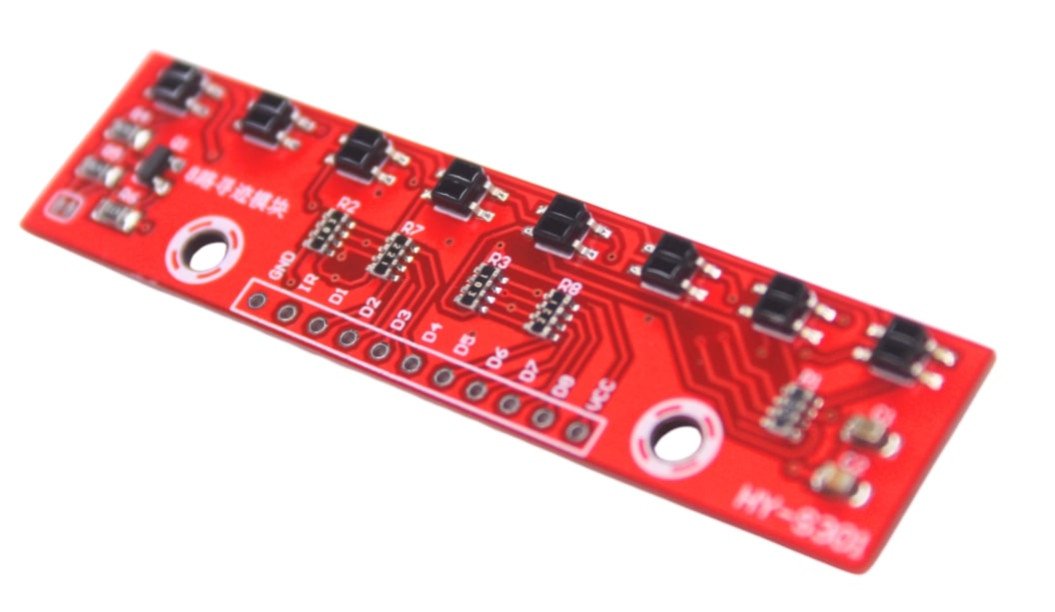
Achieve unparalleled precision in line-following robotics and automated systems with our advanced 8-Channel Infrared Line Tracking Sensor Module. This high-resolution IR detection trace sensor board is an indispensable component for any project requiring accurate path recognition, obstacle avoidance, and precise navigation. Equipped with eight independent infrared emitter/phototransistor pairs, this module offers a superior level of detail for detecting contrasting lines (typically black on white or vice-versa) compared to single or fewer channel sensors.
Each of the eight sensors operates by emitting infrared light and measuring the reflection intensity from the surface beneath. Dark surfaces, like a black line, absorb more IR light, resulting in less reflection, while lighter surfaces reflect more. The module provides digital outputs (and often analog outputs on more advanced versions), which can be directly interfaced with microcontrollers such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP32, and other development boards. This allows your robot or system to quickly interpret the line's position and make real-time adjustments for smooth and accurate tracking, even around sharp turns and complex intersections (T-junctions, cross-junctions). Many models feature onboard LEDs to visually indicate the status of each sensor, aiding in easy debugging and calibration. With its wide sensing array, our 8-Channel IR line tracking sensor is ideal for competitive line follower robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), smart car navigation, maze-solving robots, and a variety of industrial automation tasks. Its robust design and high sensitivity ensure reliable performance across different lighting conditions and surface materials. Upgrade your robotics projects with this essential sensor for enhanced intelligence and flawless path execution.
The 8-Channel Line Tracking Sensor Module is a compact, efficient solution for building intelligent robotic cars, line followers, and path tracing bots. It features 8 IR transmitter-receiver pairs, each capable of detecting high-contrast lines, typically black on white backgrounds.
Each sensor’s output can be connected to a microcontroller's GPIO pin, and digital logic levels are used to determine if the sensor detects a line. The onboard sensitivity control allows you to fine-tune performance for different surface materials and lighting conditions.
This module is ideal for advanced robot navigation, path recognition, and obstacle detection projects.
Key Features:
-
8 individual infrared (IR) sensors on a single board
-
Detects black lines on white surfaces and vice versa
-
Works with Arduino, ESP32, Raspberry Pi, STM32, and robotics kits
-
Adjustable sensitivity via onboard potentiometers
-
Digital or analog output options (depending on model)
-
Easy to mount on robot chassis for line-following applications
Technical Specifications:
| Parameter |
Specification |
| Number of Channels |
8 Infrared sensors |
| Operating Voltage |
3.3V – 5V DC |
| Output Type |
Digital (HIGH or LOW based on line detection) |
| Sensor Type |
IR LED (emitter) + Photodiode (receiver) |
| Detection Range |
0.1 – 1 cm (optimal for flat surfaces) |
| Interface |
8 digital outputs + VCC & GND |
| Adjustment |
Sensitivity adjustable (via potentiometers) |
| Board Dimensions |
~100mm × 15mm (varies by manufacturer) |
| Mounting Holes |
Yes (for easy robot chassis attachment) |
How to Use:
-
Connect VCC and GND to 5V and GND on Arduino.
-
Connect D0–D7 pins (sensor outputs) to Arduino digital input pins.
-
Read values using digitalRead() in your Arduino code.
-
Use sensor values to decide robot direction (left/right/straight).
-
Adjust each potentiometer to fine-tune detection accuracy.
Example Use: Build a smart robot car that can follow black tape on a white surface using real-time sensor feedback.
Example Circuit (Arduino Integration):
- The 8-channel line tracking sensor can easily be interfaced with platforms like Arduino using the digital input pins to read the sensor's output.
- The sensors can be connected to an Arduino board’s digital input pins (for example, pins 2-9), and the Arduino code can monitor the states of the sensors to control motors for line-following.
Arduino Code Concept Example:
// Define the sensor pins
int sensorPins[] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; // Digital pins connected to sensor
int sensorState[8]; // Array to store sensor states
void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
pinMode(sensorPins[i], INPUT); // Set all sensor pins as inputs
}
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read all sensor values
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
sensorState[i] = digitalRead(sensorPins[i]);
}
// Print sensor states to Serial Monitor
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
Serial.print(sensorState[i]);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
// Based on sensor states, you can control motors to follow the line
// (code for motor control logic goes here)
delay(100); // Small delay before next loop
}
Applications:
-
Line follower robots
-
Path recognition systems
-
Robotic automation and navigation
-
Obstacle and edge detection
-
DIY electronics, STEM kits, and school robotics
-
Arduino, ESP32, and Raspberry Pi robotics
Package Includes: